This article was written by Berkeley AI Research (BAIR) Laboratory.
Abstract
We investigate conditional adversarial networks as a general-purpose solution to image-to-image translation problems. These networks not only learn the mapping from input image to output image, but also learn a loss func- tion to train this mapping. This makes it possible to apply the same generic approach to problems that traditionally would require very different loss formulations. We demon- strate that this approach is effective at synthesizing photos from label maps, reconstructing objects from edge maps, and colorizing images, among other tasks. Indeed, since the release of the pix2pix software associated with this pa- per, a large number of internet users (many of them artists) have posted their own experiments with our system, further demonstrating its wide applicability and ease of adoption without the need for parameter tweaking. As a community, we no longer hand-engineer our mapping functions, and this work suggests we can achieve reasonable results without hand-engineering our loss functions either.
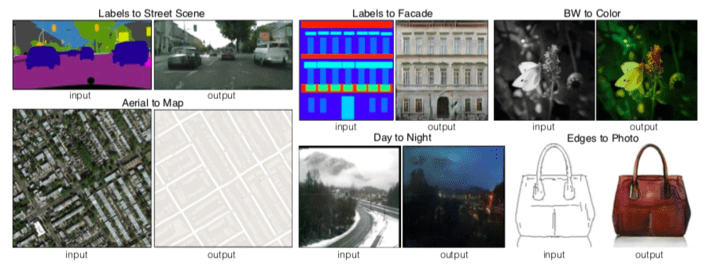
Table of contents
1. Introduction
2. Related work
3. Method
3.1. Objective
3.2. Network architectures
3.2.1 Generator with skips
3.2.2 Markovian discriminator (PatchGAN)
3.3. Optimization and inference
4. Experiments
4.1. Evaluation metrics
4.2. Analysis of the objective function
4.3. Analysis of the generator architecture
4.4. From PixelGANs to PatchGANs to ImageGANs
4.5. Perceptual validation
4.6. Semantic segmentation
4.7. Community-driven Research
5. Conclusion
To read the whole article, with each point detailed and illustrated, click here.
DSC Ressources
- Free Book and Resources for DSC Members
- New Perspectives on Statistical Distributions and Deep Learning
- Deep Analytical Thinking and Data Science Wizardry
- Statistical Concepts Explained in Simple English
- Machine Learning Concepts Explained in One Picture
- Comprehensive Repository of Data Science and ML Resources
- Advanced Machine Learning with Basic Excel
- Difference between ML, Data Science, AI, Deep Learning, and Statistics
- Selected Business Analytics, Data Science and ML articles
- Hire a Data Scientist | Search DSC | Find a Job
- Post a Blog | Forum Questions
