
- Smart city tourism uses big data and AI to provide a range of tourist services.
- Cities are jumping the gap from real-life into the metaverse.
- The technology has the potential to solve a multitude of logistic and environmental concerns.
The advent of the Metaverse—along with Covid travel restrictions and social distancing—has seen an explosion of interest in the smart city tourism concept. As well as providing innovative experiences and improving residents’ quality of life, smart tourism cities may be the ultimate solution to overtourism.
What is Smart City Tourism?
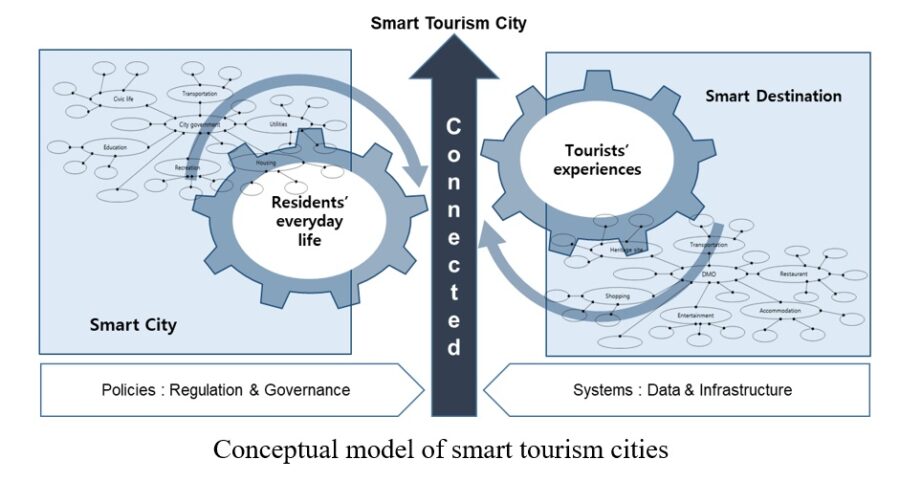
A smart tourism city uses big data, artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), and many other smart technologies to make a city more connected, efficient, interactive, and transparent [1]. A city that has implemented smart tourism can provide services, content, and information to tourists. For example, if you’re lost on the way to Tokyo, a smartphone app can help you find your way. Unsure what that obelisk is on the river Thames? There’s an app for that.
Many cities have incorporated some aspects of “Smart” to their tourism sector, including Barcelona, which has interactive bus shelters, and Brisbane, which has more than 100 points of interest integrated through a mobile app [2]. London, U.K. has been carrying out the Smart London Plan since 2013 [3], with a focus on open data and digital technologies. London’s multifaceted plan includes Visit London—a tour guide application that uses big data to provide personalized experiences for tourists.
A multitude of cities are taking the smart concept a step further, blending augmented reality (AR) with virtual reality (VR) experiences. AR is where digital displays, descriptions, and guides navigate the user through an experience in the real-world. For example, an interactive kiosk in New York City can help you find your way to The Empire State Building. On the other hand, a VR experience takes place entirely in the metaverse; As an example, it’s possible to experience walking inside an Egyptian tomb without stepping foot out of your living room.
Many cities have already developed entire worlds in the metaverse, including:
- The Finnish capital of Helsinki, which entered the metaverse in 2018 with a photorealistic digital replica of the city. The explorable digital setting is accessible via VR headsets like Oculus as well as a YouTube 360 video [4].
- Seoul, South Korea, already known as a pioneering smart city, announced a plan to enter the metaverse in 2023. VR headsets will enable users to attend cultural events, shop, and watch city official congregations.
- Also in South Korea, the city of Incheon has designed an impressive smart city comprised of two separate AR and VR experiences [5]. The VR part of Incheon’s development, dubbed “Incheoncraft” is created through Minecraft, a sandbox game which players explore a virtual world freely as avatars, allowing tourists to experience Incheon without a physical visit.

Combatting Overtourism & Improving Quality of Life
While the primary goal of a smart city is to use technology to enhance tourist attractions and accessibility [6], a secondary goal is to enhance a sustainable quality of life for city residents [2]. Overtourism puts a massive strain on urban infrastructures and poorly managed tourism fuels discontent of residents [7]. Smart city tourism creates an environment that is more sustainable, with efficient management solutions and mobility. For example, availability of transportation can be adjusted in real-time at tourist bottlenecks, dispersing tourists more evenly around the city. In addition, better social policies ensure safety and well-being as well as enabling sustainable development. These measures improve quality-of-life for city residents, making conflicts over resource use between residents and tourists less likely to arise [1].
AR and VR experiences are just two of many ways that smart city tourism is going to continue to develop going forward. As we begin to return to normal after years of lockdowns and traveling restrictions, travel will begin to boom again. The difference will be that with the smart city concept, tourism will enable more people to travel than ever before yet leaving a smaller environmental footprint.
References
- Smart tourism cities: a duality of place where technology supports the convergence of touristic and residential experiences
- Smart tourism: foundations and developments
- Smart London Plan
- Virtual Helsinki
- Travel Incheon as a Metaverse: Smart Tourism Cities Development Case in Korea
- Smart tourism cities’ competitiveness index: a conceptual model.
- Dodds, R., & Butler, R. (Eds.). (2019). Overtourism: Issues, realities and solutions. De Gruyter, Oldenbourg.
