
“The development of full artificial intelligence (AI) could spell the end of the human race. It would take off on its own and re-design itself at an ever increasing rate. Humans, who are limited by slow biological evolution, couldn’t compete and would be superseded.”
— Stephen Hawking told the BBC
Now, I love Stephen Hawking and his way of thinking. Here is a person who seems able to look around corners to predict the future. But even Willie Mays didn’t bat 1000. And I just don’t buy this statement. Why?
“Only 18% of insurers can optimize data use for competitive advantage.”
Now think about this statement: Only 18% of insurers – organizations whose business is built upon actuaries who use advanced analytics to model and predict risk – only 18% are successfully optimizing data for competitive advantage. Heck, actuaries might be the world’s first data scientists.
And we already know that movies love to popularize stories of evil AI run amuck (Figure 1).

Figure 1: Evil AI in Movies
Here is a sampling of my favorite, rewatchable evil AI movies:
- Eagle Eye: An AI super brain (ARIIA) uses Big Data and IOT to nefariously influence humans’ decisions and actions.
- I, Robot: Way cool looking autonomous robots continuously learn and evolve empowered by a cloud-based AI overlord (VIKI).
- The Terminator: An autonomous human killing machine stays true to its AI Utility Function in seeking out and killing a specific human target, no matter the unintended consequences.
- Colossus: The Forbin Project: An American AI supercomputer learns to collaborate with a Russian AI supercomputer to protect humans from killing themselves, much to the chagrin of humans who are intent on killing themselves.
- War Games: The WOPR (War Operation Plan Response) AI system learns through game playing that the only smart nuclear war strategy is “not to play”.
- 2001: The AI-powered HAL supercomputer optimizes its AI Utility Function to accomplish its prime directive, again no matter the unintended consequences.
Let’s stop over-positioning and over-promising the capabilities of AI. AI is only a tool, just like a hammer, a saw, or a backhoe (guess Hollywood hasn’t found a market for evil backhoes running amuck and taking over the world).
Before we dive into AI the tool, let’s understand how AI has been positioned vis-à-vis the wide variety of other analytic tools that are available to today’s modern business carpenters.
Analytics Maturity Index: From Operational to Autonomous Analytics
It is important that everyone learns what can be done with advanced analytic capabilities like Machine Learning, Neural Networks, and AI. While there are multiple ways to define the advanced analytics topology, I use Figure 2 to discuss the differences with my students.
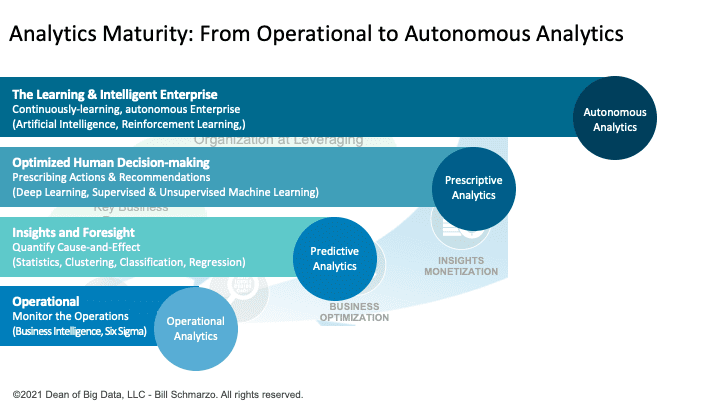
Figure 2: Analytics Maturity: From Operational to Autonomous Analytics
The Analytics Maturity Index covers the following analytic categories:
- Operational analytics monitor the operations of the business. This includes Business Intelligence (management reports and operational dashboards) and Six Sigma.
- Predictive analytics seek to quantify cause-and-effect and determine goodness of fit using Statistics to support hypothesis testing to model outcomes and Data Mining to uncover statistically significant relationships buried in large data sets.
- Prescription analytics seek to predict likely outcomes using Deep Learning (Neural Networks) to recognize “things” out of complex data formats (images, voice, audio, video, waves) and Machine Learning to identify and quantify trends, patterns, and relationships buried in the data.
- Autonomous analytics seek to continuously learn and adapt with minimal human intervention using Reinforcement Learning and Artificial Intelligence that power actions within a controlled environment to maximize rewards while minimizing costs.
Exciting? Yes! Understanding how AI works? Simple.
How Does AI Work
AI is really a very simple concept: AI just tries to optimize the decisions it has to make by continuously learning and adapting based upon interactions with its environment (Figure 3).
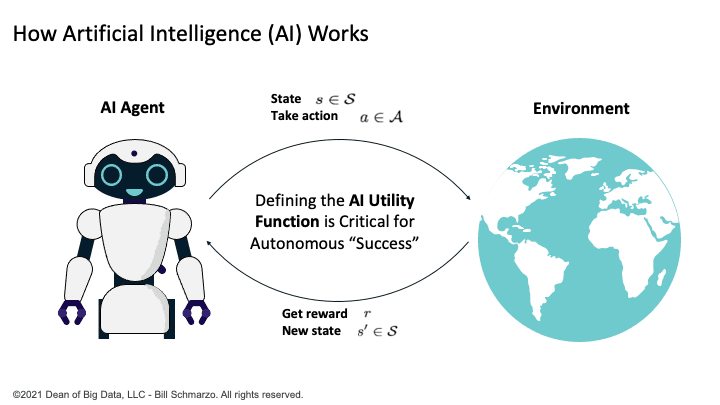
Figure 3: How Artificial Intelligence (AI) Works
AI models learn through the following process:
- An AI Engineer (collaborating with business stakeholders) defines the AI Utility Function, which are the KPIs and metrics against which AI model’s effectiveness will be measured.
- The AI model operates and interacts within its environment using the AI Utility Function to gain feedback to continuously learn and adapt its performance (using backpropagation and stochastic gradient descent to constantly tweak the models’ weights and biases).
- The AI model seeks to make the “right” or optimal decisions, as framed by the AI Utility Function, as the AI model interacts with its environment.
AI models are really doing nothing more than playing the kids’ game of “Hotter / Colder”. AI models seek to maximize “rewards” based upon the definitions of “value” as articulated in the AI Utility Function (Figure 4).
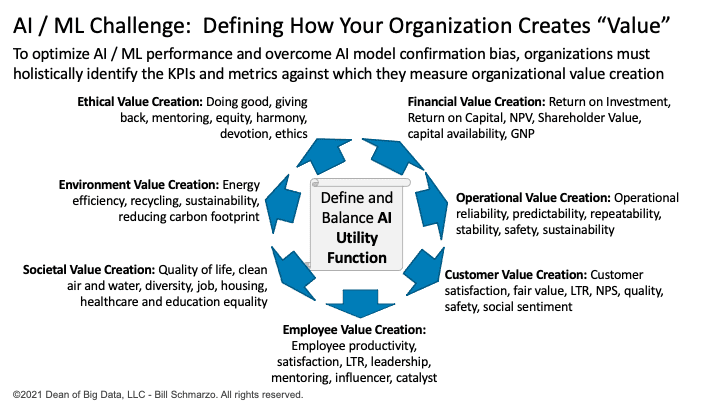
Figure 4: Define and Balance AI Utility Function
The AI model’s competence to take “intelligent” actions is based upon “value” as defined by the AI Utility Function.
For example, the Roomba Model 980 uses AI (Reinforcement Learning) to transverse the house, identify obstacles, and remember which routes work best to clean the house. It builds a map of the house and uses each vacuuming excursion to refine and update that map (Figure 5).
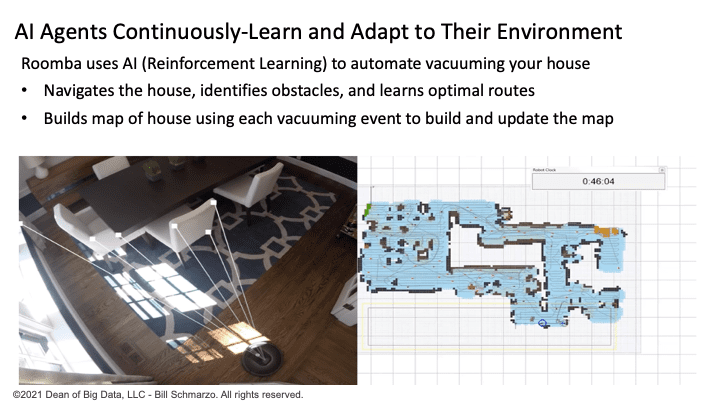
Figure 5: Roomba Using AI / Reinforcement Learning to Autonomously Vacuum Your Home
Summary: 10 Human Behaviors for Humans to Thrive in a World of AI
Not sure why 10 is some magically number (Number of fingers on your hand? Number of frames in bowlin’? Bo Derek?), but here is my list of the top 10 human behaviors that can overcome that massive learning advantage that AI models have over us humans (Figure 6).
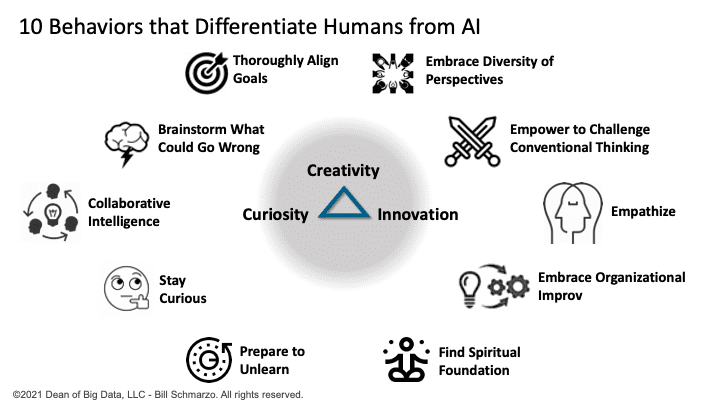
Figure 6: 10 Behaviors that Differentiate Humans from AI
I’d recommend “What Movies Can Teach Us About Prospering in an AI World – Part 2” if you are seeking ways to differentiate yourself from these hyper-fast learning machines. Probably our best chance to ensure that AI works for us versus us working for AI.
